题目描述
给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
- 创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
- 递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
- 递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
0 <= nums[i] <= 1000
nums 中的所有整数 互不相同
样例
示例 1:
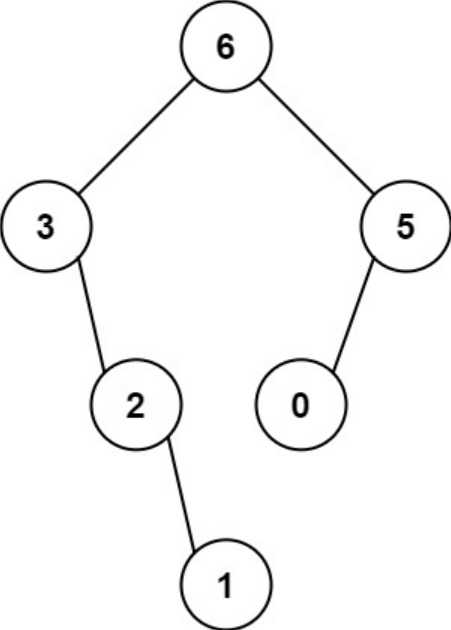
输入:nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5]
输出:[6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
解释:递归调用如下所示:
- [3,2,1,6,0,5] 中的最大值是 6 ,左边部分是 [3,2,1] ,右边部分是 [0,5] 。
- [3,2,1] 中的最大值是 3 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [2,1]
- 空数组,无子节点。
- [2,1] 中的最大值是 2 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [1] 。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 1 的节点。
- [0,5] 中的最大值是 5 ,左边部分是 [0] ,右边部分是 [] 。
- 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 0 的节点。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- [3,2,1] 中的最大值是 3 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [2,1]
示例 2:
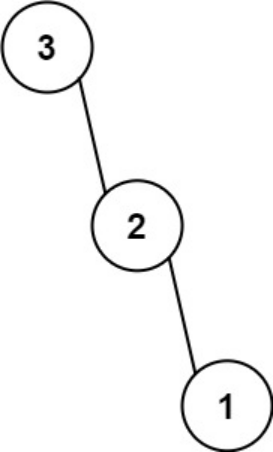
输入:nums = [3,2,1]
输出:[3,null,2,null,1]
题目评估
知识点:栈、树、数组、分治、二叉树、单调栈
难度:中等
分析
本题使用分支递归解题,找到当前数组中最大值递归最大值左边的数组和右边的数组并连接在左子树和右子树。
Java代码题解
分治递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return plantTrees(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
// 递归方法
private TreeNode plantTrees(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
int rootIndex = findMaxIndex(nums, start, end);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[rootIndex]);
if (start < rootIndex) {
root.left = plantTrees(nums, start, rootIndex - 1);
}
if (end > rootIndex) {
root.right = plantTrees(nums, rootIndex + 1, end);
}
return root;
}
// 找到数组中的最大值的下标
private int findMaxIndex(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int index = start;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) {
max = nums[i];
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
}
单调栈:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return monotonicallyStack(nums);
}
private TreeNode monotonicallyStack(int[] nums) {
// 单调栈
TreeNode[] stack = new TreeNode[nums.length];
// 栈顶指针
int point = 0;
for (int n : nums) {
// 当前节点
TreeNode tn = new TreeNode(n);
// 当栈顶元素小于当前值,不断弹栈,将当前元素的left指向栈顶元素
while (point > 0 && stack[point - 1].val < n) {
tn.left = stack[point - 1];
// 栈顶指针下移
point--;
}
// 栈内有节点,一定比当前值大,把栈顶元素的right指向当前元素
if (point > 0) {
stack[point - 1].right = tn;
}
// 当前元素入栈
stack[point] = tn;
point++;
}
return stack[0];
}
}
复杂度分析
分治递归:
时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度:O(n)
单调栈:
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)