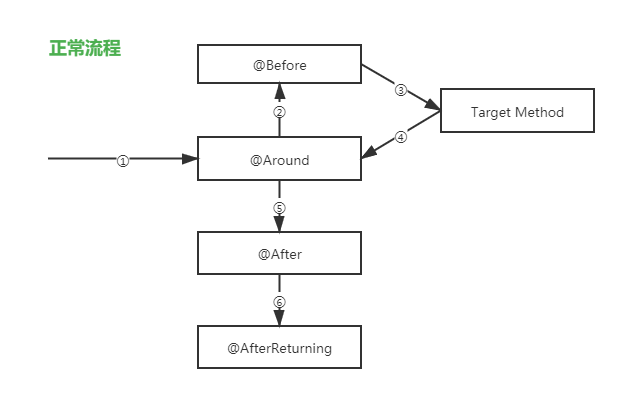
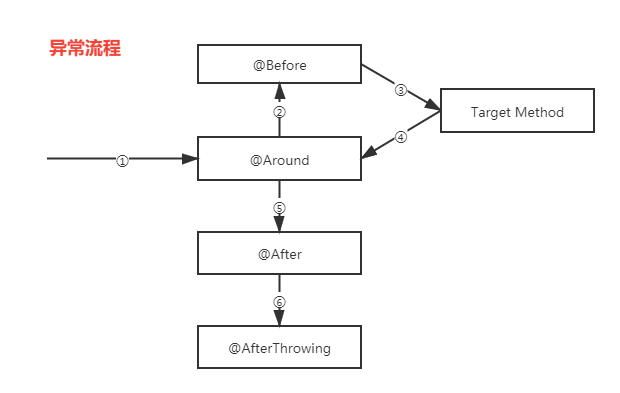
1 前情提要
注:在以后章节,不再用eclipse和单纯的Spring项目,将使用Idea和SpringBoot结合Maven项目继续学习。SpringBoot是Spring的封装,它将繁琐的Spring配置自动化,无需程序员再手动配置浪费时间的各种参数。Maven是依赖管理工具,它不需用我们人为的为项目导入各种jar包,只需要我们在它的配置文件即pom文件中加入几小行xml配置即可导入对应的依赖。以上IOC的内容中各种手动配置的容器参数以及导入jar包等操作,在SpringBoot项目和Maven项目中均可省略。
2 AOP简介
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
出处
3 OOP和AOP的关系
AOP和OOP不存在谁取代谁的关系,它们是相互促进相互补充,AOP是在不改变OOP类代码的基础上对原有的类方法功能进行拓展。
4 AOP中的概念
通知Advice:拓展的功能就是通知,本质:方法。
切面Aspect:通知所在的类就是切面,本质:类。
切入点Point Cut:指定通知对谁进行拓展,本质:表达式。
连接点Join Point:通知和目标方法的交点。
织入Weaving:将通知应用到目标方法的过程。
目标对象Target:目标方法所在的类对象。
5 AOP问题实现
- 第一步:导入jar包(Maven项目不用,在pom文件中配置会自动导入,如下)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
</dependency>
- 第二部:将拓展的类和切面类放入到Spring容器中(SpringBoot项目不用,它会自动扫描然后放入容器,前提是加了注解)
- 在切面类加@Aspect注解,同时在Spring配置文件中开启基于注解的切面支持(SpringBoot项目不用,它没有繁琐的配置)
- 在切面中写通知,并指定切入点表达式
CommonBean.java 一个被容器管理的bean
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CommonBean {
public double add(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("method start running");
double sum = i + j;
System.out.println("method end run");
return sum;
}
}
LogAspect.java 一个切面
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
@Before(value = "execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("method before...");
}
@After(value = "execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("method after...");
}
}
AspectTest.java 一个SpringBoot测试类
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class AspectTest {
@Autowired
CommonBean commonBean;
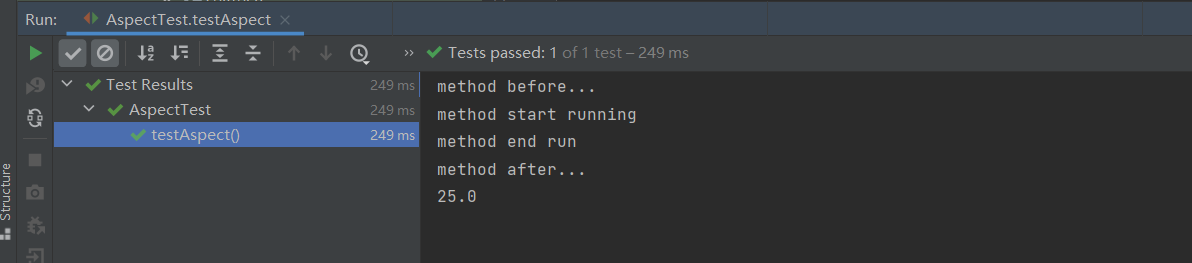
@Test
public void testAspect() {
double sum = commonBean.add(10, 15);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
控制台打印结果:
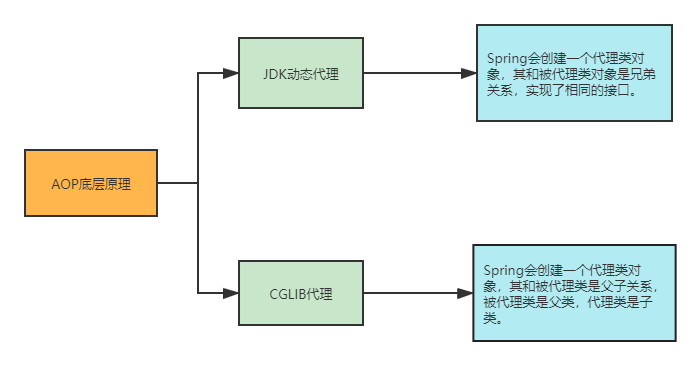
6 AOP的底层原理
AOP是通过类的代理来实现的。类的代理可以通过两种方式,具体如下图:
7 切面中的四种通知
7.1 前置通知
@Before:在目标方法执行之前执行。
注释:@Before("execution(访问权限修饰符 返回类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数类型1, 参数类型2, ...))")
示例:@Before(value = "execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
如5.4应用
7.2 后置通知
@After:无论目标方法有没有执行成功,在目标方法执行结束后,后置通知都会执行。
注释:@After("execution(访问权限修饰符 返回类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数类型1, 参数类型2, ...))")
示例:@After("execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
7.3 返回通知
@AfterReturning:在目标方法执行成功之后,返回通知才会执行。所以该通知和AfterThrowing通知只能执行其中一个。
注释:@AfterReturning("execution(访问权限修饰符 返回类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数类型1, 参数类型2, ...))")
示例:@AfterReturning("execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
7.4 异常通知
@AfterThrowing:在目标方法执行失败之后,异常通知才会执行。所以该通知和AfterReturning通知只能执行其中一个。
注释:@AfterThrowing("execution(访问权限修饰符 返回类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数类型1, 参数类型2, ...))")
示例:@AfterThrowing("execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
7.5 举例演示以上通知
编写切面类:LogAspect.java
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
@Before(value = "execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("Advice method before...");
}
@After(value = "execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("Advice method after...");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("Advice method afterReturning...");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("Advice method afterThrowing...");
}
}
将目标方法中的加法修改为除法以便于抛出除以0异常:CommonBean.java
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CommonBean {
public double add(int i, int j) {
System.out.println("method start running");
double sum = i / j; // 这里修改为除法
System.out.println("method end run");
return sum;
}
}
测试类:AspectTest.java
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class AspectTest {
@Autowired
private CommonBean commonBean;
@Test
public void testAspect() {
double sum = commonBean.add(1, 1);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
运行结果:
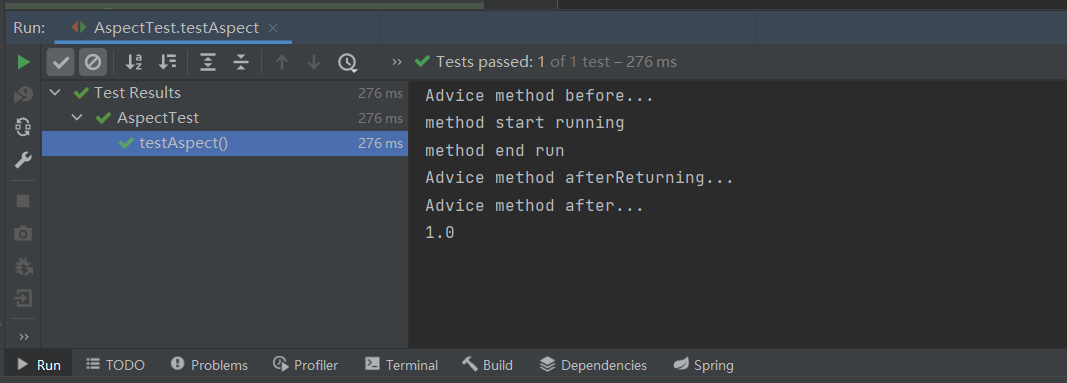
可以看到上方运行结果一切正常,除了异常通知没有执行其他通知全部执行。现在修改第二个参数为0,让一个数字除以0抛出异常。
测试类:AspectTest.java
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class AspectTest {
@Autowired
private CommonBean commonBean;
@Test
public void testAspect() {
double sum = commonBean.add(1, 0); // 这里除以0
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
运行结果:
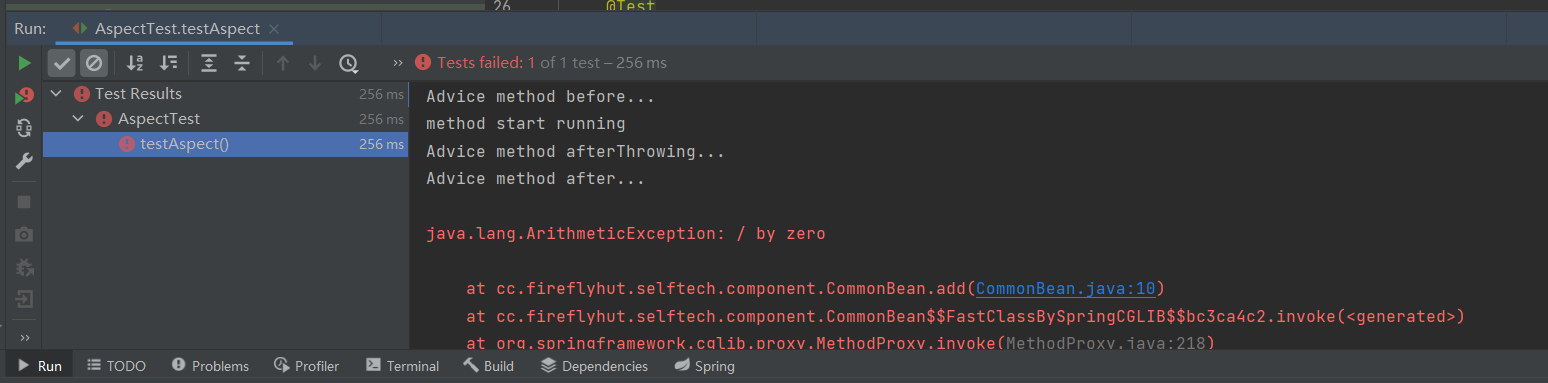
可以看到程序抛出ArithmeticException异常,返回通知没有执行,取而代之的是异常通知。
8 切入点表达式
8.1 切入点表达式的语法
提前声明:方法签名 = 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表)
-
最精确匹配
语法:execution(访问权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法签名)
示例:execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int)) -
最模糊匹配
语法:execution(* *.*(..))
说明:第一个星指定任意权限修饰符和任意返回值类型。第二个星指定任意类。第三个星指定任意方法。两个点点指定任意类型的参数列表。 -
当前包及其子包匹配
语法:execution(* 包名..*(..))
示例:execution(* cc.fireflyhut.selftech..*(..))
说明:匹配当前包及其子包的类中的所有方法。要在包名后加两个点。如要指定方法只需将第二个星修改即可 -
后缀匹配
语法:execution(访问权限修饰符 返回值类型 包名.*类名后缀.*方法名后缀(参数列表))
示例:execution(* cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.*Bean.*Method(..))
说明:匹配cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component包下类名以Bean为后缀的类中方法名以Method为后缀的方法。 -
前缀匹配
语法:execution(访问权限修饰符 返回值类型 包名.类名前缀*.方法名前缀*(参数列表))
示例:execution(* cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.Common*.only*(..))
说明:同后缀匹配类似,匹配cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component包下类名以Common为前缀的类中方法名以only为前缀的方法。 -
继承匹配
语法:execution(访问权限修饰符 返回值类型 包名.类名+.方法名(参数类型+, ..))
示例:execution(* cc.fireflyhut.selftech.service.CommonService+.*(Object+, ..))
说明:匹配实现了CommonService接口的所有类及其接口本身中的参数列表第一个参数是Object子类的所有方法。
8.2 切入点表达式的重用
当我们想在一个切点加入多个通知时需要重复写多个切入点表达式,重复性很高,于是我们可以通过@Pointcut注释来提取复用切入点表达式减少重复性。
改写切面类,加入切入点方法:LogAspect.java
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
// 定义一个方法取代切入点表达式
@Pointcut("execution(public double cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean.add(int, int))")
public void pointCut() {}
// 改写以下通知的切入点表达式为切入点表达式的方法名
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("Advice method before...");
}
@After("pointCut()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("Advice method after...");
}
@AfterReturning("pointCut()")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("Advice method afterReturning...");
}
@AfterThrowing("pointCut()")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("Advice method afterThrowing...");
}
}
测试类:AspectTest.java
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.component.CommonBean;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class AspectTest {
@Autowired
private CommonBean commonBean;
@Test
public void testAspect() {
double sum = commonBean.add(1, 1);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
执行结果和不复用是一样的:
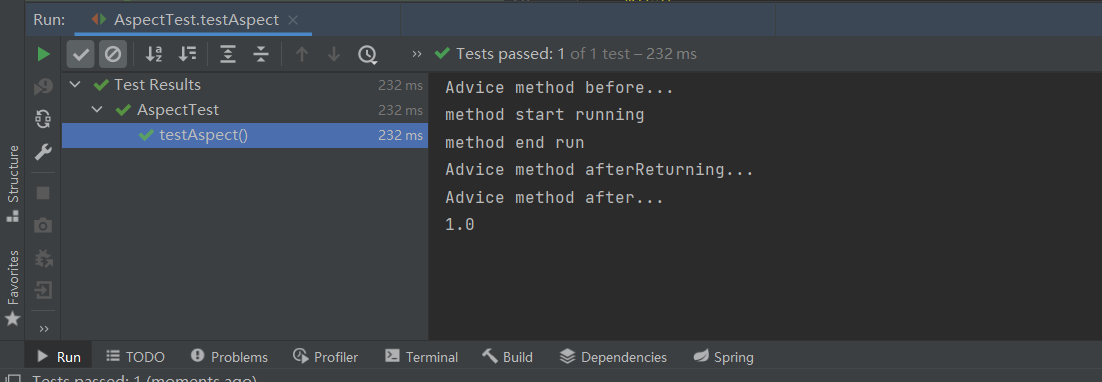
9 从通知中获取目标方法信息
在Before通知中可以通过JoinPoint对象获得目标方法的参数列表、方法签名等等信息。
在AfterReturning通知中可以通过@AfterReturning注解的returning属性并在方法参数列表中定义同该属性值一致的参数来获得返回值信息。
在AfterThrowing通知中可以通过@AfterThrowing注解的throwing属性并在方法参数列表中定义同该属值一致的参数来获得异常信息。
下面用几个示例来说明。
接口CommonService.java
public interface CommonService {
public String justRun(String someInfo, int someNum, int anotherNum);
}
接口实现类CommonServiceImpl.java
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.service.CommonService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CommonServiceImpl implements CommonService {
@Override
public String justRun(String someInfo, int someNum, int anotherNum) {
int retNum = someNum / anotherNum;
String ret = someInfo + " And " + retNum;
System.out.println(ret);
return ret;
}
}
切面类ServiceAspect.java
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@Component
@Aspect
public class ServiceAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* cc.fireflyhut.selftech.service.CommonService+.*(..))")
public void pointCut() {}
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Advice before...");
// 获得目标方法参数列表
List<Object> argList = Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs());
// 获得方法签名
Signature methodSignature = joinPoint.getSignature();
// 获得方法名
String methodName = methodSignature.getName();
System.out.println("方法签名:" + methodSignature);
System.out.println("方法名:" + methodName);
System.out.println("参数列表:" + argList);
}
@After("pointCut()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("Advice after...");
}
/**
* 1. 要在@AfterReturning注解中加入returning属性
* 2. 返回值要用Object类型接收
* 3. 参数名字和returning属性的值要一致
* */
@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()", returning = "result")
public void afterReturning(Object result) {
System.out.println("Advice afterReturning...");
System.out.println("返回结果:" + result);
}
/**
* 1. 要在@AfterThrowing注解中加入throwing属性
* 2. 异常信息要用Throwable类型接收
* 3. 参数名字和throwing属性值要一致
* */
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()", throwing = "exception")
public void afterThrowing(Throwable exception) {
System.out.println("Advice afterThrowing...");
System.out.println("异常信息:" + exception.getMessage());
}
}
测试类AspectTest.java
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.service.CommonService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class AspectTest {
@Autowired
private CommonService commonService;
@Test
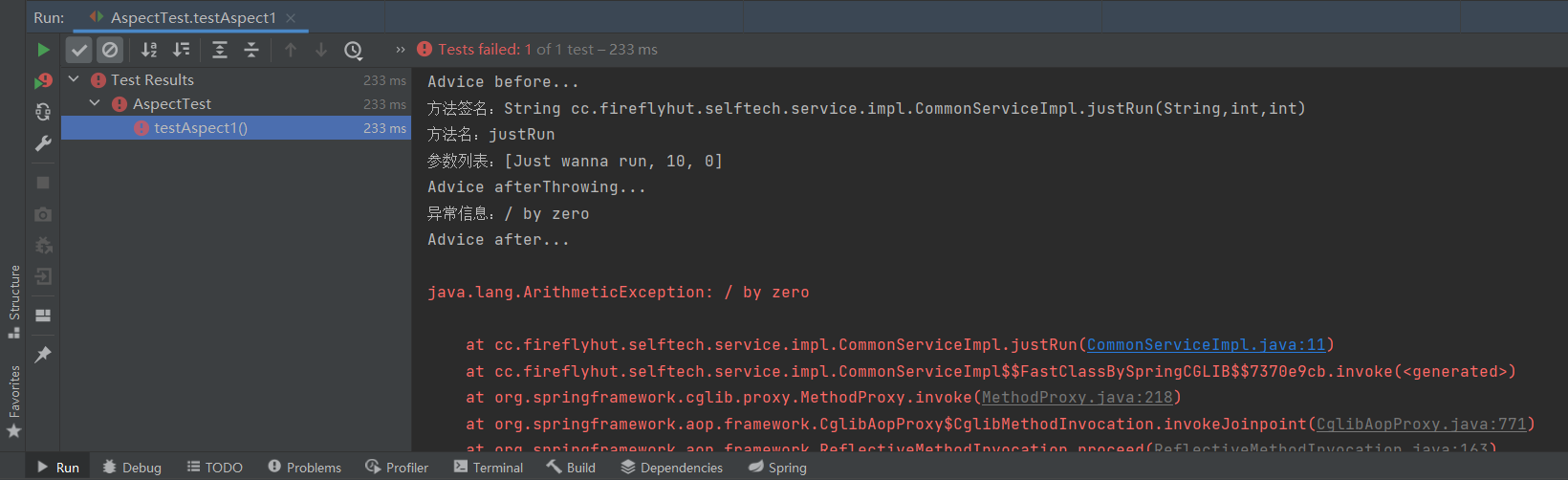
public void testAspect1() {
commonService.justRun("Just wanna run", 10, 2);
//commonService.justRun("Just wanna run", 10, 0);
}
}
正常执行结果:
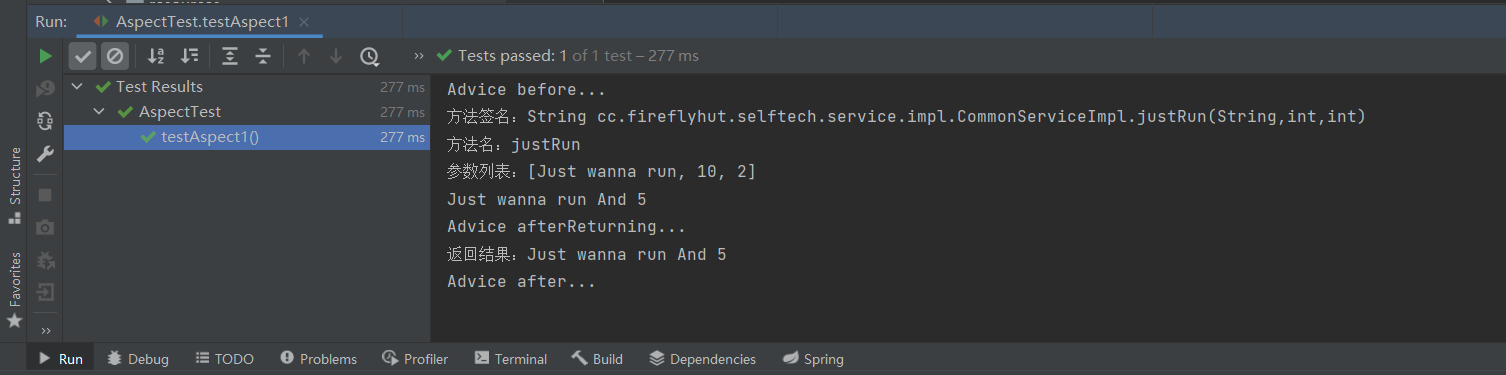
异常执行结果:
10 Around注解增强处理
通过上面四个注解的介绍,虽然可以增加编程的便利性减少冗余性,但是功能还不够整合,于是我们介绍下面一个注解@Around注解。
下面介绍一下@Around注解
10.1 Around注解的作用
- 既可以在目标方法之前织入增强动作,也可以在执行目标方法之后织入增强动作。
- 可以决定目标方法在什么时候执行,如何执行,甚至可以完全阻止目标目标方法的执行。
- 可以改变执行目标方法的参数值,也可以改变执行目标方法之后的返回值。当需要改变目标方法的返回值时,只能使用@Around注解。
注意:虽然@Around功能强大,但通常需要在线程安全的环境下使用。因此,如果使用普通的@Before、@AfterReturing注解就可以解决的事情,就没有必要使用@Around增强处理了。
10.2 Around注解的使用演示
10.2.1 增强Around注解的使用方法
- 首先自定义一个注解MyAnnotation.java:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 运行时有效
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 作用于方法
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String something() default "";
}
- 再定义一个切面ControllerAspect.java:
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class ControllerAspect {
/**
* 增强模式的Around通知,它通过自定义的注解来匹配切入点
* */
@Around(value = "@annotation(myAnnotation)") // 注意这里的属性值要定义和方法参数一样的名字
public Object aroundByEnhance(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, MyAnnotation myAnnotation) throws Throwable {
// 我们可以通过注解实例来获取到注解属性的值
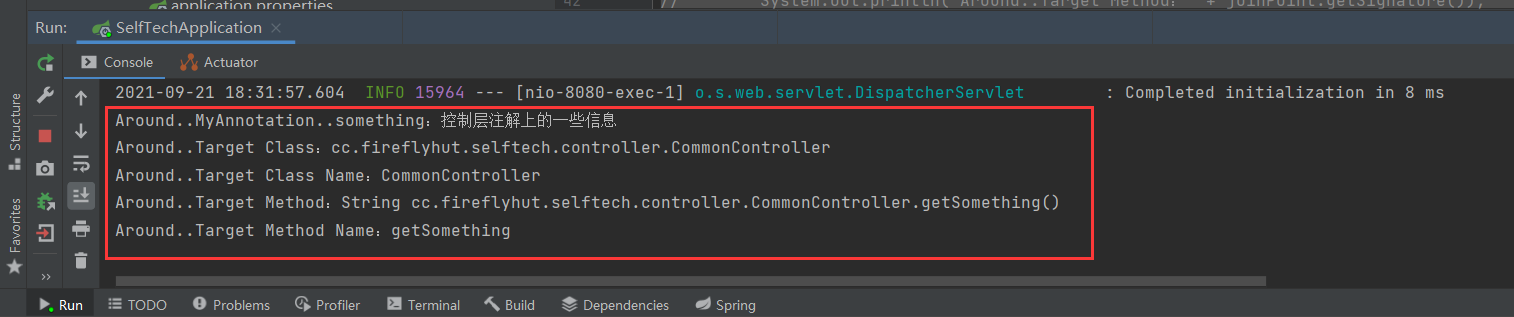
System.out.println("Around..MyAnnotation..something:" + myAnnotation.something());
System.out.println("Around..Target Class:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
System.out.println("Around..Target Class Name:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("Around..Target Method:" + joinPoint.getSignature());
System.out.println("Around..Target Method Name:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
- 最后定义一个Controller用作演示CommonController.java:
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class CommonController {
@PostMapping("/part1")
@ResponseBody
@MyAnnotation(something = "控制层注解上的一些信息") // 这里加上我们自定义的注解并在属性中传值
public String getSomething() {
return "{\"msg\":\"success\"}";
}
}
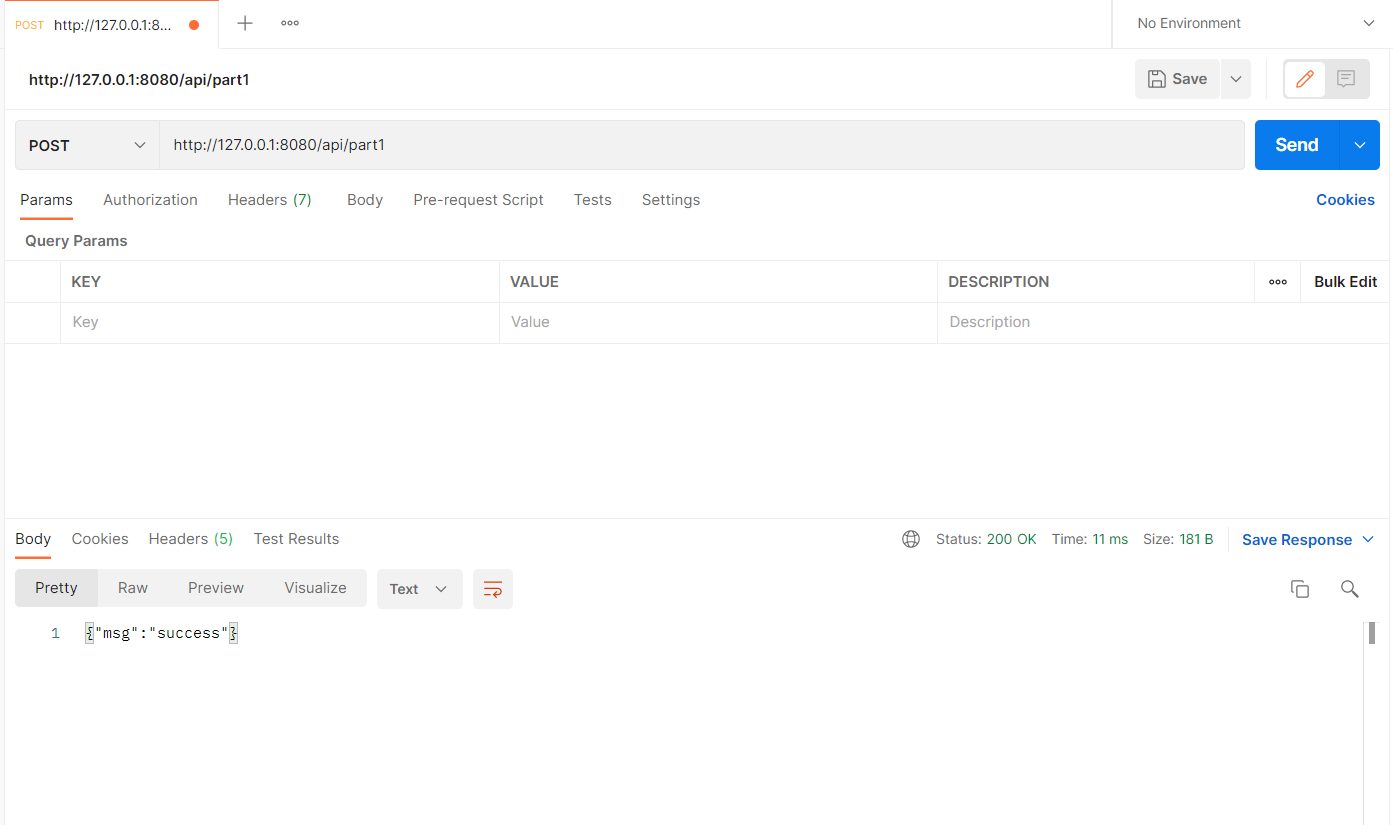
- 发送请求查看结果:
我们通过postman发送请求可以查看到返回的结果:
我们再在Idea控制台可以看到通知打印的内容:
10.2.2 Around注解的常规使用方法
相对于增强方式我们只需要改动切面类中的一些内容
- 修改切面类ControllerAspect.java
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class ControllerAspect {
/**
* 增强模式的Around通知,它通过自定义的注解来匹配切入点
* */
@Around(value = "@annotation(myAnnotation)") // 注意这里的属性值要定义和方法参数一样的名字
public Object aroundByEnhance(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, MyAnnotation myAnnotation) throws Throwable {
// 我们可以通过注解实例来获取到注解属性的值
System.out.println("Around..MyAnnotation..something:" + myAnnotation.something());
System.out.println("Around..Target Class:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
System.out.println("Around..Target Class Name:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("Around..Target Method:" + joinPoint.getSignature());
System.out.println("Around..Target Method Name:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
// 常规使用方法增加以下内容
/**
* 通过切入点表达式定义切点
* */
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* cc.fireflyhut.selftech.controller.CommonController.*(..))")
public void pointCut() {}
/**
* 常规模式的Around通知,它通过切入点表达式匹配目标方法
* */
@Around(value = "pointCut()")
public Object arountByCommon(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
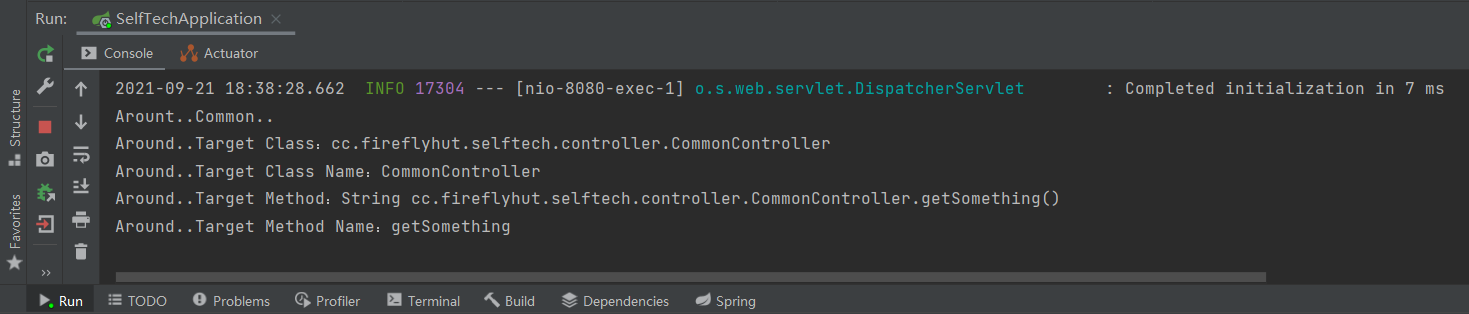
System.out.println("Arount..Common..");
System.out.println("Around..Target Class:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
System.out.println("Around..Target Class Name:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("Around..Target Method:" + joinPoint.getSignature());
System.out.println("Around..Target Method Name:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
- 修改控制层方法,将自定义注解注释掉CommonController.java
import cc.fireflyhut.selftech.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class CommonController {
@PostMapping("/part1")
@ResponseBody
//@MyAnnotation(something = "控制层注解上的一些信息") // 这里加上我们自定义的注解并在属性中传值
public String getSomething() {
return "{\"msg\":\"success\"}";
}
}
- 再次使用postman发送请求查看结果:
一切都在意料之中
11 各个通知及其目标方法的执行顺序